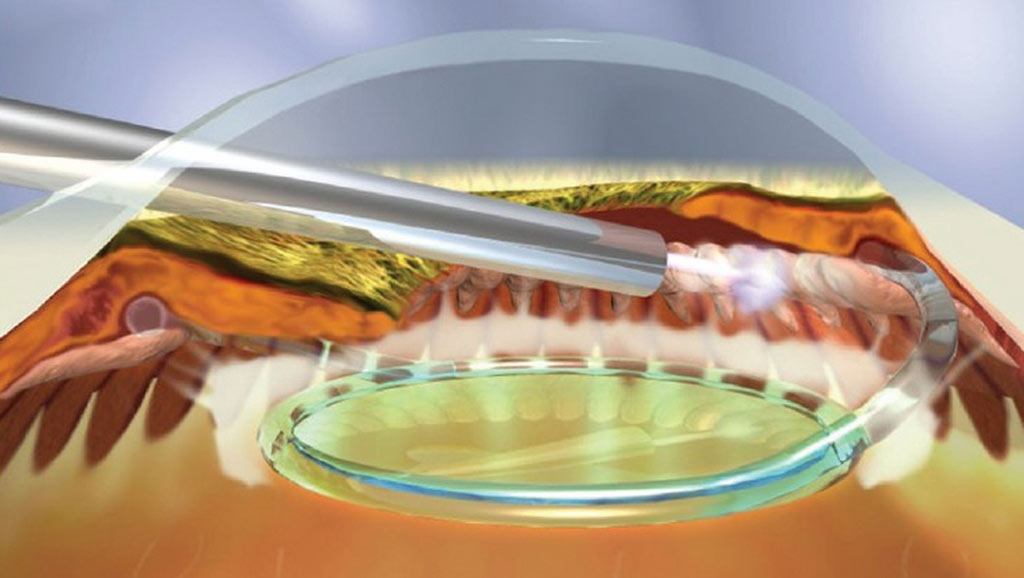
Diode Cyclophotocoagulation (CPC)
Diode Cyclophotocoagulation (CPC) is recommended for patients with refractory glaucoma to reduce aqueous humor secretion and lower IOP by lasering the secretory epithelium of the ciliary body.
Why would Cyclophotocoagulation be recommended for me?
Cyclophotocoagulation is recommended for patients with refractory glaucoma who have persistent elevated eye pressure. Patients usually have failed tube shunt procedures or trabeculectomies. Some patients have minimal useful vision. The procedure may be used on patients with no visual potential and a need for pain relief.
Diode cyclophotocoagulation is an outpatient procedure. The patient receives a peribulbar block (anesthesia around the eye) prior to the laser. The laser, performed by your ophthalmic surgeon, takes 20 to 30 minutes and will require use of postoperative drops to decrease inflammation in the eye. Most patients have minimal postoperative pain. The procedure is often combined with injection of a pain killer (Chlorpromazine) behind the eye ball.
Since there are no incisions made into the eyeball there are usually no postoperative restrictions associated with the procedure. You will have a patch on the eye for the first 24 hours after the procedure and your doctor will want to see you the day following the procedure in the office to check your eye pressure.
CPC may be repeated if the desired eye pressure is not achieved.

 DONATE NOW
DONATE NOW